Ancient Civilisations
Ancient Rome
Resource Key
When accessing content use the numbers below to guide you
 LEVEL 1
LEVEL 1
Brief, basic information laid out in an easy-to-read format. May use informal language. (Includes most news articles)
 LEVEL 2
LEVEL 2
Provides additional background information and further reading. Introduces some subject-specific language
 LEVEL 3
LEVEL 3
Lengthy, detailed information. Frequently uses technical/subject-specific language. (Includes most analytical articles)
What is an Artefact?

Reference Generator
Remember to use the Reference Generator to build your bibliography as you research.
Access all your resources through Nexus – it’s your go-to for the LibGuide and digital tools
Ancient Artifacts

The following articles are from the Informit database and are of a high reading level. However, they contain valuable information that you can use for your assessment
Maps
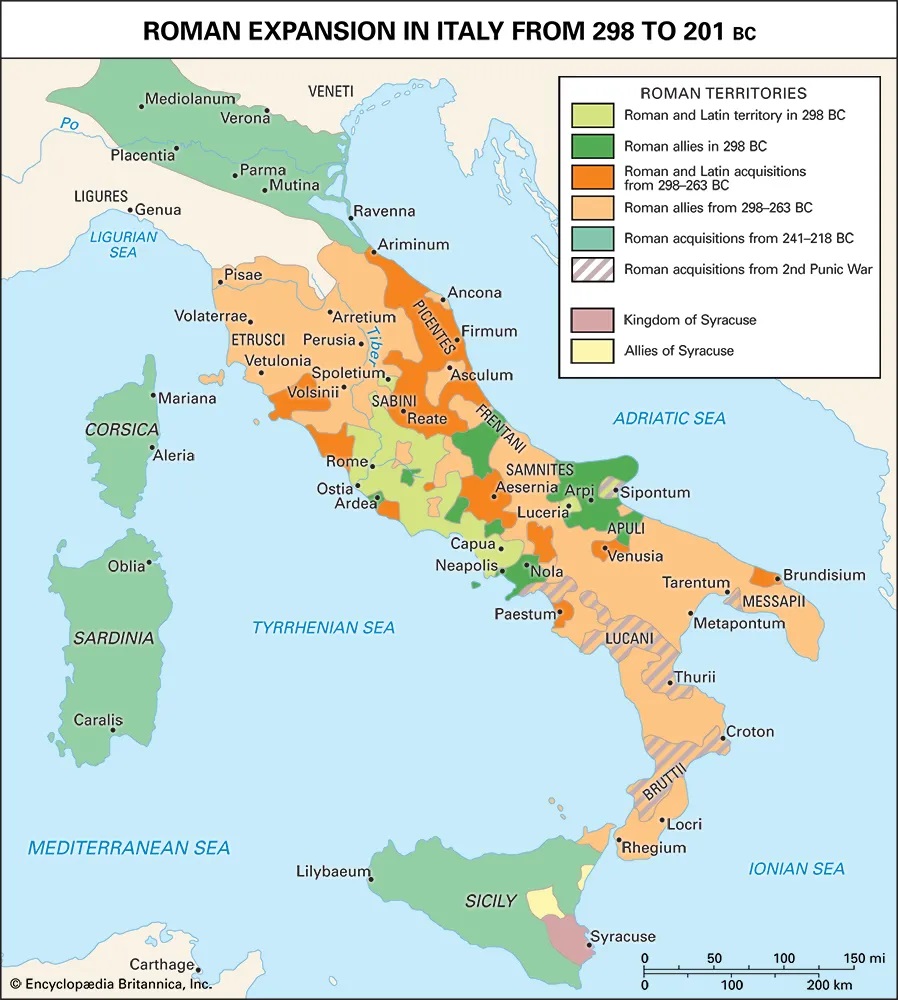
Encyclopædia Britannica. (n.d.). ancient Rome, 3rd century bc . [image]. Britannica School. Retrieved September 2, 2025, from https://school.eb.com.au/levels/middle/assembly/view/183134
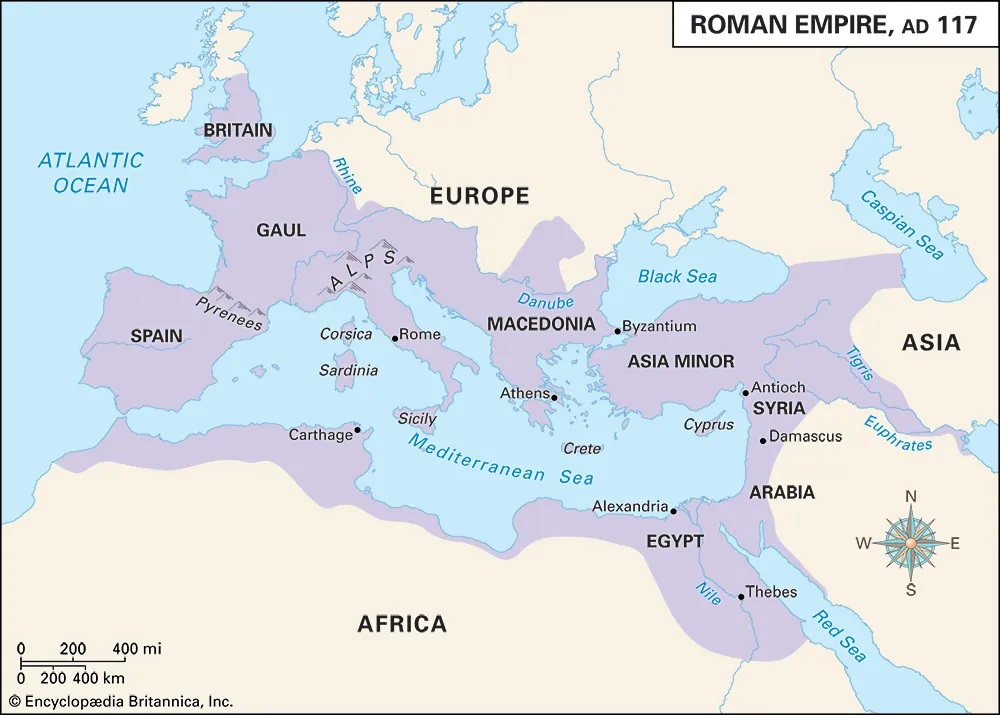
Encyclopædia Britannica. (n.d.). Roman Empire . [image]. Britannica School. Retrieved September 2, 2025, from https://school.eb.com.au/levels/middle/assembly/view/183129
Videos

Web Links

-
Roman Artifacts – 10 Famous MasterpiecesThe story of the Roman Empire, which spanned hundreds of years and numerous continents, is documented through the ancient Roman artifacts left behind by its residents.
-
Top 10 Artifacts from Ancient RomeThe Portland Vase is a famous example of Roman glasswork, thought to date from between 5 BCE and 25 AD.
-
Roman Artifacts – A Glimpse into Ancient RomeRoman artifacts come in many different shapes and sizes. There are various ancient Roman antiques, artworks, and other artifacts to explore from this ancient and long-lasting civilization.
Nexus-S Resources

The British Museum
The British Museum in London has many fascinating artefacts from Ancient Rome, especially from Roman Britain.
These objects help us understand how Romans lived, worked, and ate nearly 2,000 years ago.
Some examples include:
- Roman coins – used for trade and showing emperors' faces.
- Pottery and cooking tools – like frying pans, moratorium (grinding bowls), and cheese presses.
- Gardening tools – such as spades, hoes, and pruning hooks used to grow crops like garlic, lettuce, and cucumber.
- Writing tablets – used for messages and records.
- Statues and stonework – showing Roman gods and important people.
- Baby bottles and eating utensils – showing how families cared for children and shared meals.
These artefacts show that Roman life was both advanced and surprisingly similar to ours today.
Visiting the British Museum lets us explore how Romans shaped Britain and left behind tools, art, and ideas we still use.







